精彩评论
- 张麻子是杂种(6天前)
从有人以来就没有比张麻子更邪恶 张口闭口为人民,害死几千万人还为人民,为自己的皇位还差不多,...
评:深度解析《让子弹飞》 al2359(3年前 (2023-02-06))
求科学离线插件,谢谢!34401355@qq.com
评:改版梅林固件安装SS【shadowsocks】科学上网插件教程al2359(3年前 (2023-02-06))
求科学离线插件,谢谢!!!
评:改版梅林固件安装SS【shadowsocks】科学上网插件教程

FFMpeg 作为音视频领域的开源工具,它几乎可以实现所有针对音视频的处理,本文主要利用 FFMpeg 官方提供的 SDK 实现音视频最简单的几个实例:编码、解码、封装、解封装、转码、缩放以及添加水印。
接下来会由发现问题->分析问题->解决问题->实现方案,循序渐进的完成。
参考代码:ffmpeg_sdk
本例子实现的是将视频域 YUV 数据编码为压缩域的帧数据,编码格式包含了 H.264/H.265/MPEG1/MPEG2 四种 CODEC 类型。 实现的过程,可以大致用如下图表示:
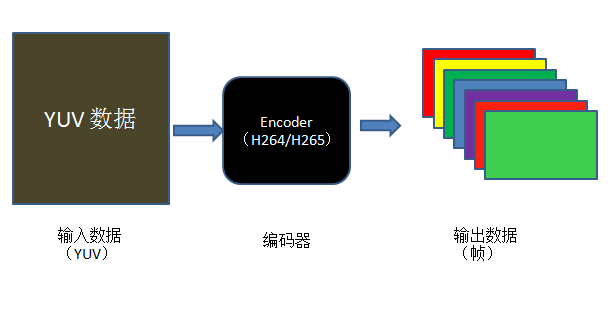
从图中可以大致看出视频编码的流程:
根据流程可以推倒出大致的代码实现:
AVFrame 结构体的分配使用av_frame_alloc()函数,该函数会对 AVFrame 结构体的某些字段设置默认值,它会返回一个指向 AVFrame 的指针或 NULL指针(失败)。AVFrame 结构体的释放只能通过av_frame_free()来完成。注意,该函数只能分配 AVFrame 结构体本身,不能分配它的 data buffers 字段指向的内容,该字段的指向要根据视频的宽高、像素格式信息手动分配,本例使用的是av_image_alloc()函数。代码实现大致如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
//allocate AVFrame struct
AVFrame *frame = NULL;
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if(!frame){
printf("Alloc Frame Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//fill AVFrame struct fields
frame->width = width;
frame->height = height;
frame->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
//allocate AVFrame data buffers field point
ret = av_image_alloc(frame->data, frame->linesize, frame->width, frame->height, frame->pix_fmt, 32);
if(ret < 0){
printf("Alloc Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//write input file data to frame->data buffer
fread(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width*frame->height, pInput_File);
...
av_frame_free(frame);
|
编解码器相关的 AVCodec 结构体的分配使用avcodec_find_encoder(enum AVCodecID id)完成,该函数的作用是找到一个与 AVCodecID 匹配的已注册过得编码器;成功则返回一个指向 AVCodec ID 的指针,失败返回 NULL 指针。该函数的作用是确定系统中是否有该编码器,只是能够使用编码器进行特定格式编码的最基本的条件,要想使用它,至少要完成两个步骤:
针对第一步中关于编解码器的特定参数,FFMpeg 提供了一个专门用来存放 AVCodec 所需要的配置参数的结构体 AVCodecContext 结构。它的分配使用avcodec_alloc_context3(const AVCodec *codec)完成,该函数根据特定的 CODEC 分配一个 AVCodecContext 结构体,并设置一些字段为默认参数,成功则返回指向 AVCodecContext 结构体的指针,失败则返回 NULL 指针。分配完成后,根据视频特性,手动指定与编码器相关的一些参数,比如视频宽高、像素格式、比特率、GOP 大小等。最后根据参数信息,打开找到的编码器,此处使用avcodec_open2()函数完成。代码实现大致如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
AVCodec *codec = NULL;
AVCodecContext *codecCtx = NULL;
//register all encoder and decoder
avcodec_register_all();
//find the encoder
codec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id);
if(!codec){
printf("Could Not Find the Encoder\n");
return -1;
}
//allocate the AVCodecContext and fill it's fields
codecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if(!codecCtx){
printf("Alloc AVCodecCtx Fail\n");
return -1;
}
codecCtx->bit_rate = 4000000;
codecCtx->width = frameWidth;
codecCtx->height = frameHeight;
codecCtx->time_base= (AVRational){1, 25};
//open the encoder
if(avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, NULL) < 0){
printf("Open Encoder Fail\n");
}
|
存放编码数据的结构体为 AVPacket,使用之前要对该结构体进行初始化,初始化函数为av_init_packet(AVPacket *pkt),该函数会初始化 AVPacket 结构体中一些字段为默认值,但它不会设置其中的 data 和 size 字段,需要单独初始化,如果此处将 data 设为 NULL、size 设为 0,编码器会自动填充这两个字段。
有了存放编码数据的结构体后,我们就可以利用编码器进行编码了。FFMpeg 提供的用于视频编码的函数为avcodec_encode_video2,它作用是编码一帧视频数据,该函数比较复杂,单独列出如下:
1 2 |
int avcodec_encode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt,
const AVFrame *frame, int *got_packet_ptr);
|
它会接收来自 AVFrame->data 的视频数据,并将编码数据放到 AVPacket->data 指向的位置,编码数据大小为 AVPacket->size。
其参数和返回值的意义:
编码完成后就可将AVPacket->data内的编码数据写到输出文件中;代码实现大致如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
AVPacket pkt;
//init AVPacket
av_init_packet(&pkt);
pkt.data = NULL;
pkt.size = 0;
//encode the image
ret = avcodec_encode_video2(codecCtx, &pkt, frame, &got_output);
if(ret < 0){
printf("Encode Fail\n");
return -1;
}
if(got_output){
fwrite(pkt.data, 1, pkt.size, pOutput_File);
}
|
编码的大致流程已经完成了,剩余的是一些收尾工作,比如释放分配的内存、结构体等等。
完整实现请移步编码实现。
解码实现的是将压缩域的视频数据解码为像素域的 YUV 数据。实现的过程,可以大致用如下图所示。
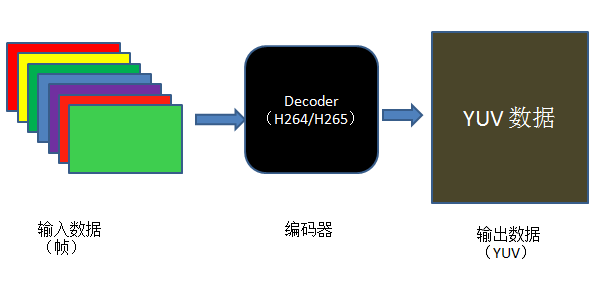
从图中可以看出,大致可以分为下面三个步骤:
根据流程可以推倒出大致的代码实现:
对于输入数据,首先,通过 fread 函数实现将固定长度的输入文件的数据存放到一块 buffer 内。H.264中一个包的长度是不定的,读取固定长度的码流通常不可能刚好读出一个包的长度;对此,FFMpeg 提供了一个 AVCoderParserContext 结构用于解析读到 buffer 内的码流信息,直到能够取出一个完整的 H.264 包。为此,FFMpeg 提供的函数为av_parser_parse2,该函数比较复杂,定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
int av_parser_parse2(AVCodecParserContext *s,
AVCodecContext *avctx,
uint8_t **poutbuf, int *poutbuf_size,
const uint8_t *buf, int buf_size,
int64_t pts, int64_t dts,
int64_t pos);
|
函数的参数和返回值含义如下:
FFMpeg 中为我们提供的该函数常用的使用方式为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
while(in_len){
len = av_parser_parse2(myparser. AVCodecContext, &data, &size, in_data, in len, pts, dts, pos);
in_data += len;
in_len -= len;
if(size)
decode_frame(data, size);
}
|
如果参数poutbuf_size的值为0,那么应继续解析缓存中剩余的码流;如果缓存中的数据全部解析后依然未能找到一个完整的包,那么继续从输入文件中读取数据到缓存,继续解析操作,直到pkt.size不为0为止。
因此,关于输入数据的处理,代码大致如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
//open input file
FILE *pInput_File = fopen(Input_FileName, "rb+");
if(!pInput_File){
printf("Open Input File Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//read compressed bitstream form file to buffer
uDataSize = fread(inbuf, 1, INBUF_SIZE, pInput_File);
if(uDataSize == 0){ //decode finish
return -1;
}
//decode the data in the buffer to AVPacket.data
while(uDataSize > 0){
len = av_parser_parse2(pCodecParserCtx, codecCtx,
&(pkt.data), &(pkt.size),
pDataPtr, uDataSize,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE);
uDataSize -= len;
uDataPtr += len;
if(pkt.size == 0) continue;
decode_frame(pkt.data, pkt.size);
}
|
注意,上面提到的av_parser_parse2函数用的几个参数,其实是与具体的编码格式有关的,它们应该在之前已经分配好了,我们只是放到后面来讲一下,因为它们是与具体的解码器强相关的。
对于解码器。与上面提到的编码实现类似,首先,根据 CODEC_ID 找到注册的解码器 AVCodec,FFMpeg 为此提供的函数为avcodec_find_decoder();其次,根据找到的解码器获取与之相关的解码器上下文结构体 AVCodecC,使用的函数为编码中提到的avcodec_alloc_context3;再者,如上面提到的要获取完整的一个 NALU,解码器需要分配一个 AVCodecParserContext 结构,使用函数av_parser_init;最后,前面的准备工作完成后,打开解码器,即可调用 FFMpeg 提供的解码函数avcodec_decode_video2对输入的压缩域的码流进行解码,并将解码数据存放到 AVFrame->data 中。代码实现大致如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 |
AVFrame *frame = NULL;
AVCodec *codec = NULL;
AVCodecContext *codecCtx = NULL;
AVCodecParserContext *pCodecParserCtx = NULL;
//register all encoder and decoder
avcodec_register_all();
//Allocate AVFrame to Store the Decode Data
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if(!frame){
printf("Alloc Frame Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Find the AVCodec Depending on the CODEC_ID
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if(!codec){
printf("Find the Decoder Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Allocate the AVCodecContext
codecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if(!codecCtx){
printf("Alloc AVCodecCtx Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Allocate the AVCodecParserContext
pCodecParserCtx = av_parser_init(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if(!pCodecParserCtx){
printf("Alloc AVCodecParserContext Fail\n");
return -1;
}
//Open the Decoder
if(avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, NULL) < 0){
printf("Could not Open the Decoder\n");
return -1;
}
//read compressed bitstream form file to buffer
uDataSize = fread(inbuf, 1, INBUF_SIZE, pInput_File);
if(uDataSize == 0){ //decode finish
return -1;
}
//decode the data in the buffer to AVPacket.data
while(uDataSize > 0){
len = av_parser_parse2(pCodecParserCtx, codecCtx,
&(pkt.data), &(pkt.size),
pDataPtr, uDataSize,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE);
uDataSize -= len;
uDataPtr += len;
if(pkt.size == 0) continue;
//decode start
avcodec_decode_video2(codecCtx, frame, &got_frame, pkt);
}
|
注意,上面解码的过程中,针对具体的实现,可能要做一些具体参数上的调整,此处只是理清解码的流程。
对于输出数据。解码完成后,解码出来的像素域的数据存放在 AVFrame 的 data 字段内,只需要将该字段内存放的数据之间写文件到输出文件即可。解码函数avcodec_decode_video2函数完成整个解码过程,对于它简单介绍如下:
1 2 3 |
int avcodec_decode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *picture,
int *got_picture_ptr,
const AVPacket *avpkt);
|
该函数各个参数的意义:
由此可见,当标识位为1时,代表解码一帧结束,可以写数据到文件中。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
pOutput_File = fopen(Output_FileName, "wb");
if(!pOutput_File){
printf("Open Output File Fail\n");
return -1;
}
if(*got_picture_ptr){
fwrite(frame->data[0],1, Len, pOutput_File)
}
|
解码的大致流程已经完成了,剩余的是一些收尾工作,比如释放分配的内存、结构体等等。
完整实现请移步解码实现。
本例子实现的是将视频数据和音频数据,按照一定的格式封装为特定的容器,比如FLV、MKV、MP4、AVI等等。实现的过程,可以大致用如下图表示:
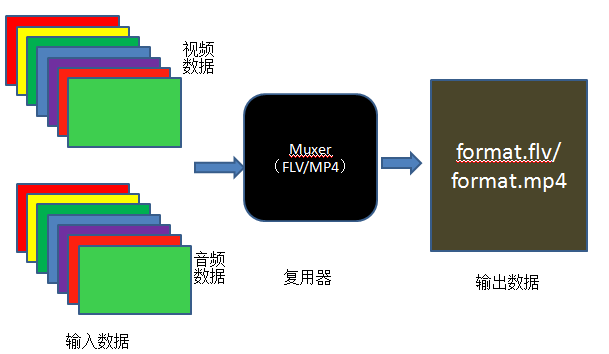
从图中可以大致看出视频封装的流程:
根据流程可以推倒出大致的代码实现:
对于由 YUV 数据得到编码的视频数据部分,不再重复。直接看与 Muxer 相关的部分,与特定的 Muxer 相关的信息,FFMpeg 提供了一个 AVFormatContext 的结构体描述,并用avformat_alloc_output_context2()函数来分配它。该函数的声明如下:
1 2 |
int avformat_alloc_output_context2(AVFormatContext **ctx, AVOutputFormat *oformat,
const char *format_name, const char *filename);
|
其中:
代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
AVOutputFormat *fmt;
AVFormatContext *oc;
/* allocate the output media context */
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, NULL, filename);
if (!oc) {
printf("Could not deduce output format from file extension: using MPEG.\n");
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&oc, NULL, "mpeg", filename);
}
if (!oc)
return 1;
fmt = oc->oformat;
|
有了表示媒体文件格式的 AVFormatContext 结构后,就需要根据媒体格式来判断是否需要往媒体文件中添加视频流、音频流(有的媒体文件,这两种流并不是必须的);以 MP4 格式的媒体文件为例,我们需要一路视频流、一路音频流。因此需要创建一路流,FFMpeg 提供的创建流的函数为avformat_new_stream(),该函数完成向 AVFormatContext 结构体中所代码的媒体文件中添加数据流,函数声明如下:
1 |
AVStream *avformat_new_stream(AVFormatContext *s, const AVCodec *c); |
其中:
注意:对于 Muxer,该函数必须在调用avformat_write_header()前调用。使用完成后,需要调用avcodec_close()和avformat_free_context()来清理由它分配的内容。
该函数调用完成后,一个新的 AVStream 便已经加入到输出文件中,下面就需要设置 stream 的 id 和 codec 等参数。以视频流为例,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
OutputStream *ost;
AVFormatContext *oc;
AVCodec **codec;
AVCodecContext *c;
AVStream *st;
st = avformat_new_stream(oc, *codec);
if(!st){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate stream\n");
exit(1);
}
st->id = oc->nb_streams-1;
c = st->codec;
|
参数设置完成后,就可以打开编码器并为编码器分配必要的内存。步骤跟之前的类似,以视频为例,示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
//open the codec
ret = avcodec_open(c, codec, &opt);
if(ret < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open video codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
}
//allocate and init a re-usable frame
ost->frame = alloc_picture(c->pix_fmt, c->width, c->height);
|
接下来进行真正的封装:首先,为媒体文件添加头部信息,FFMpeg 为此提供的函数为avformat_write_header()。其次,将编码好的音视频 AVPacket 包添加到媒体文件中去,FFMpeg 为此提供的函数为av_interleaved_write_frame()。最后,写入文件尾的数据,FFMpeg 为此提供的函数为av_write_trailer()。
封装的大致流程已经完成了,剩余的是一些收尾工作,比如释放分配的内存、结构体等等。
完整实现请移步封装实现。
本例子实现的是将音视频分离,例如将封装格式为 FLV、MKV、MP4、AVI 等封装格式的文件,将音频、视频分离开来。 实现的过程,可以大致用如下图表示:
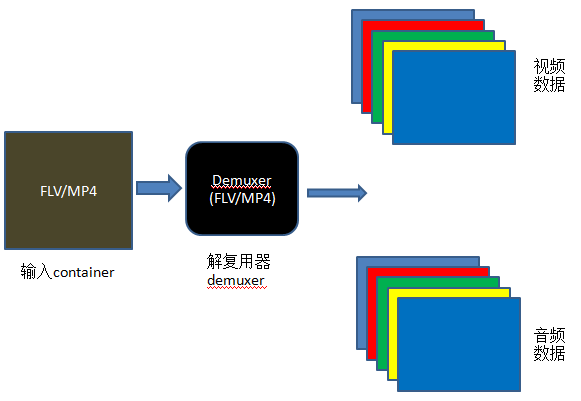
从图中可以看出大致的节封装流程:
根据流程可以推到出大致的代码流程:
在音视频分离后,需要将分离出的音视频分别放到不同的输出文件中,为此,需要打开文件以备后用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
static const char *video_dst_filename = NULL; static const char *audio_dst_filename = NULL; static FILE *video_dst_file = NULL; static FILE *audio_dst_file = NULL; video_dst_filename = argv[2]; audio_dst_filename = argv[3]; video_dst_file = fopen(video_dst_filename, "wb+"); audio_dst_file = fopen(audio_dst_filename, "wb+"); |
对于给定的需要 AV 分离的输入文件,使用avformat_open_input打开输入文件,并分配AVFormatContext结构。该函数的声明如下:
1 |
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *filename, AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options); |
其中:
实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
//open input file, and allocate format context
if(avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, src_filename, NULL, NULL) < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open source file %s\n", src_filename);
exit(1);
}
//retrive stream information
if(avformat_find_stream_info(fmt_ctx, NULL) < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find stream information\n");
exit(1);
}
|
通过输入文件分配好AVFormatContext后,需要找到里面的音频流和视频流,此处需要用到的函数为av_find_best_stream; 之后要根据找到的不同的流(如H264流、HEVC流等)找到特定的编解码器,此处使用avcodec_find_decoder;找到了解码器后, 就需要打开解码器,此处使用avcodec_open2函数完成。下面分别介绍这几个函数的使用:
av_find_best_stream函数定义如下:
1 |
int av_find_best_stream(AVFormatContext *ic, enum AVMediaType type, int wanted_stream_nb, int related_stream, AVCodec **decoder_ret, int flags); |
其中:
avcodec_find_decoder函数定义如下:
1 |
AVCodec *avcodec_find_decoder(enum AVCodecID id); |
该函数参数为AVCodecID指定了请求的解码器,成功返回解码器,否则返回 NULL。
avcodec_open2函数定义如下:
1 |
int avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVCodec *codec, AVDictionary **options); |
其中:
该函数的主要作用是根据给定的AVCodec初始化AVCodecContext,在使用该函数之前,待初始化的AVCodecContext结构需要先使用avcodec_alloc_context3分配好。其中的参数 AVCodec可以通过avcodec_find_decoder_by_nameavcodec_find_encoder_by_nameavcodec_find_decoder或avcodec_find_endcoder来获取。在进行真正的解码之前,必须调用该函数。 下面给出使用的示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
avcodec_register_all();
av_dict_set(&opts, "b", "2.5M", 0);
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if(!codec)
exit(1);
context = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if(avcodec_open2(context, codec, opts) < 0)
exit(1);
|
对于上面分析的部分,我们将其封装在一个函数里,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
static int open_codec_context(int *stream_idx,
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx,
enum AVMediaType type)
{
int ret, stream_index;
AVStream *pStream;
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = NULL;
AVCodec *codec;
ret = av_find_best_stream(fmt_ctx, type, -1, -1, NULL, 0);
if(ret < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find %s stream in input file '%s'\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type), src_filename);
}else{
stream_index = ret;
pStream = fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index];
//find decoder for the stream
codec_ctx = pStream->codec;
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(codec_ctx->codec_id);
if(!codec){
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to find %s codec\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type));
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
//open the decoder
if((ret = avcodec_open2(codec_ctx, codec, NULL))< 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open %s codec\n",
av_get_media_type_string(type));
return ret;
}
}
*stream_idx = stream_index;
}
|
针对音频、视频,分别调用该函数,示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
if(open_codec_context(&video_stream_idx, fmt_ctx, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) >= 0){
video_stream = fmt_ctx->streams[video_stream_idx];
video_codec_ctx = video_stream->codec;
//allocate image where the decoded image will be put
width = video_codec_ctx->width;
height = video_codec_ctx->height;
pix_fmt = video_codec_ctx->pix_fmt;
ret = av_image_alloc(video_dst_data, video_dst_linesize,
width, height, pix_fmt, 1);
if(ret < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate raw video buffer\n");
exit(1);
}
video_dst_bufsize = ret;
}
if(open_codec_context(&audio_stream_idx, fmt_ctx, AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) >= 0){
audio_stream = fmt_ctx->streams[audio_stream_idx];
audio_codec_ctx = audio_stream->codec;
}
|
上面的一些准备工作完成后,就需要从输入文件中一帧一帧读取数据,并进行解码了。从这里可以看出,需要找到一个 一帧视频存放的地方,为此需要使用av_init_packet初始化一个AVPacket。之后就可以使用av_read_frame来从输入 文件中读取一个 frame。示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
static int decode_packet(int *got_frame, int cached)
{
int ret = 0;
int decoded = pkt.size;
*got_frame = 0;
if(pkt.stream_index == video_stream_idx){
//decode video frame
ret = avcodec_decode_video2(video_codec_ctx, frame, got_frame, &pkt);
if(ret < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Error decoding video frame (%s) \n",
av_err2str(ret));
return ret;
}
printf("num %d got_frame %d\n", num++, *got_frame);
if(*got_frame){
av_image_copy(video_dst_data, video_dst_linesize,
(const uint8_t **)(frame->data), frame->linesize,
pix_fmt, width, height);
//write to raw video file
fwrite(video_dst_data[0], 1, video_dst_bufsize, video_dst_file);
}
}else if(pkt.stream_index == audio_stream_idx){
//decode audio frame
ret = avcodec_decode_audio4(audio_codec_ctx, frame, got_frame, &pkt);
if(ret < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Error decoding audio frame (%s)\n", av_err2str(ret));
return ret;
}
if(*got_frame){
size_t unpadded_linesize = frame->nb_samples * av_get_bytes_per_sample(frame->format);
fwrite(frame->extended_data[0], 1, unpadded_linesize, audio_dst_file);
}
}
return FFMIN(ret, pkt.size);
}
//allocate frame
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if(!frame){
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate frame\n");
exit(1);
}
av_init_packet(&pkt);
pkt.data = NULL;
pkt.size = 0;
//read frames from the file
int got_frame;
while(av_read_frame(fmt_ctx, &pkt) >= 0){
AVPacket orig_pkt = pkt;
do{
ret = decode_packet(&got_frame, 0);
if(ret < 0)
break;
pkt.data += ret;
pkt.size -= ret;
}while(pkt.size > 0);
av_free_packet(&orig_pkt);
}
|
解封装大致流程已经完成了,剩余的是一些收尾工作,例如释放刚刚分配的内存等。
完整实现过程请移步解封在实现.
针对视频的缩放,FFMpeg 提供了 libswscale 库,可以轻松实现视频的分辨率转换功能。除此之外,libswscale 库还可以 实现颜色空间转换的功能。
FFMpeg 中针对视频的缩放提供了一个示例代码,位于doc\examples\scaling_video.c中。分析该程序的流程大致分为如下几部分:
首先解析期望的视频宽高,示例代码中使用的是av_parse_video_size函数,该函数的声明如下:
1 |
int av_parse_video_size(int *width_ptr, int *height_ptr, const char *str); |
解析 str,并将解析出来的宽高信息赋值给 width_ptr, height_ptr;其中:
之后,创建SwsContext结构体,示例代码中使用的是sws_getContext函数,该函数声明如下:
1 2 3 4 |
struct SwsContext *sws_getContext(int srcW, int srcH, enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat,
int dstW, int dstH, enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat,
int flags, SwsFilter *srcFilter,
SwsFilter *dstFilter, const double *param);
|
该函数的作用是分配并返回一个SwsContext结构,后面如果需要实现缩放/转换操作时,需要使用sws_scale函数。其中:
编译时用make examples后生成 scaling_video 可执行文件。命令行如下:
1 |
$ /scaling_video 001_bit_rv8_64P_352x288.yuv hd1080 |
注意,输入时 YUV 数据,输出时 RGB 数据,会根据后面的 size 生成不同分辨率的数据。
「梦想一旦被付诸行动,就会变得神圣,如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请帮助本站成长」
上一篇:欧丽娟教授:不读书的人,人生会缺少什么?受益匪浅,值得看一看!
下一篇:黄杨钿甜,“天价耳环”事件全过程
从有人以来就没有比张麻子更邪恶 张口闭口为人民,害死几千万人还为人民,为自己的皇位还差不多,...
评:深度解析《让子弹飞》求科学离线插件,谢谢!34401355@qq.com
评:改版梅林固件安装SS【shadowsocks】科学上网插件教程求科学离线插件,谢谢!!!
评:改版梅林固件安装SS【shadowsocks】科学上网插件教程